POSCAR 与其他格式互转
大约 2 分钟
POSCAR 与其他格式互转
将 POSCAR 转换为 xsd 格式文件
该方法依赖 ASE。
ASE 的 ase.io.read() 与 ase.io.write()
ase.io.read() 与 ase.io.write(),文档见 File input and output — ASE documentation (dtu.dk)
ase.io.read()
【功能为:Read Atoms object(s) from file】
官方关于 ase.io.read() 的使用为:
ase.io.read(filename: Union[str, pathlib.PurePath, IO], index: Optional[Any] = None, format: Optional[str] = None, parallel: bool = True, do_not_split_by_at_sign: bool = False, **kwargs)
一般我们只需要提供 文件名称及其类型 就行,比如:
ase.io.read(filename, format=files_format)
如,我需要读取文件‘POSCAR’,文件类型为‘vasp’,则函数调用时应为:
ase.io.read('POSCAR, format='vasp')
ase.io.write()
【功能为:Write Atoms object(s) to file】
官方关于 ase.io.write() 的使用为:
ase.io.write(filename: Union[str, pathlib.PurePath, IO], images: Union[ase.atoms.Atoms, Sequence[ase.atoms.Atoms]], format: Optional[str] = None, parallel: bool = True, append: bool = False, **kwargs: dict)
其使用与 ase.io.read() 的相类似,不同地是 需要指定需要写入文件的 atoms objects,其实就是原子信息,输入的类型可以是 Atoms object or list of Atoms objects。由 ase.io.read() 函数可以知道,一份有关原子信息的文件其实就是 atoms object。所以:
ase.io.write(‘test.xsd’, atoms object,format='xsd')
这里 test. xsd 是希望得到的文件格式的文件名 + 后缀名,POSCAR 是指读取的文件,format='xsd' 是指信息写入文件的文件类型。
所以 ase 转换文件格式的原理 是:
- 先读取文件中的所有信息,转为 atoms object
- 再将 atoms object 写入其他格式的文件中
单份 poscar 文件转换为 xsd 文件
比如,由 VASP 得到一份 POSCAR 文件,这里实现将其文件格式转换为 xsd 格式的文件,文件名为 test。
代码思路就是 (调用 ase.io 模块):
- 使用 read() 函数读取文件信息,暂存为 atoms object
- 接着使用 write() 函数将该 atoms object 写入文件
from ase.io import read,write
poscar_file=read('POSCAR',format='vasp')
xsd_file=write('test.xsd',poscar_file,format='xsd')
注意:文件名需要带有文件格式后缀
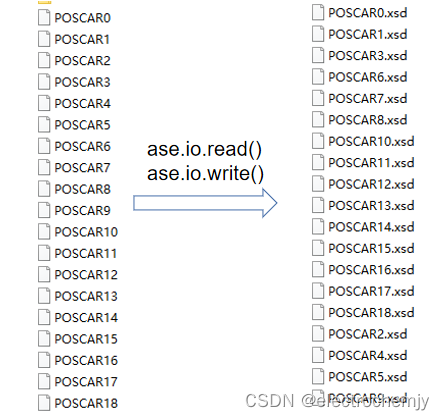
将多份 poscar 文件转换为 xsd 文件
结合 for 循环遍历文件输入\输出 atoms object,即可实现批量操作。
def poscar_to_xsd(file_PATH):
#file_PATH为储存所有待转换格式的文件的文件夹路径
tqdm=os.listdir(file_PATH)#文件夹中的文件列表
for i in range(0,len(tqdm)):#逐次遍历文件夹下的文件
inputfile = os.path.join(file_PATH,tqdm[i])#对应文件夹下的某份文件
outputfile=inputfile+'.xsd'#定义转换格式后的文件名字
poscar_file=read(inputfile,format='vasp')#读入文件
xsd_file=write(outputfile,poscar_file,format='xsd')#将读入的文件写入其他格式的文件
#调用该函数
poscar_to_xsd("C-N-2-defect-1652750340")